We are supported by our audience. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, at no extra cost for you. Learn more. Last update on 30th June 2025 / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API.
You’ll achieve ideal paint stripping results by selecting chemical agents that match your miniature’s material and paint type. Methylene chloride-based strippers aggressively swell paint films up to 10 times but pose toxicity risks, while biodegradable alternatives like soy methyl ester preserve delicate resin details safely. Essential techniques include ultrasonic cleaning for intricate surfaces, manual scraping with specialized tools, and controlled heat application. Always wear chemical-resistant gloves and work in ventilated areas. The complete process requires understanding layer thickness, paint chemistry, and proper post-treatment preparation for successful results.
Notable Insights
- Choose appropriate chemical strippers like methylene chloride-based or acetone depending on paint type and miniature material composition.
- Use manual scraping tools, ultrasonic cleaners, or controlled heat guns for effective paint removal without damaging delicate surfaces.
- Wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and respirators while working in well-ventilated areas to prevent health risks.
- Consider biodegradable stripping solutions and water-based techniques as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional harsh chemical removers.
- Allow adequate soaking time and use multiple treatment cycles for stubborn coatings, especially on older paints.
Common Chemical Stripping Agents and Their Effectiveness
When selecting chemical stripping agents for miniature paint removal, you’ll encounter five primary categories that vary markedly in effectiveness and application suitability.
Methylene chloride-based strippers offer aggressive action, swelling paint films up to 10 times their original volume, but present significant toxicity risks.
Methylene chloride strippers deliver powerful paint removal through dramatic film swelling but require careful handling due to severe health hazards.
Acetone and nail polish removers provide strong solvent capabilities against enamel and acrylic paints, though their chemical interactions can damage plastic substrates.
Cold chemical strippers operate at room temperature using biodegradable formulations, balancing efficacy with substrate preservation.
High-temperature strippers excel on stubborn coatings but risk melting delicate plastics.
Biphasic strippers employ dual-phase chemistry for complex paint compatibility scenarios. Modern chemical solutions focus on enhanced waste reduction while maintaining effective paint removal performance.
Emulsion cleaners combine solvent and aqueous cleaning abilities, making them particularly suitable for delicate miniature surfaces without harsh pH exposure.
Your choice depends on paint type, substrate material, and safety requirements, with eco-friendly alternatives increasingly preferred.
Essential Paint Removal Techniques and Methods
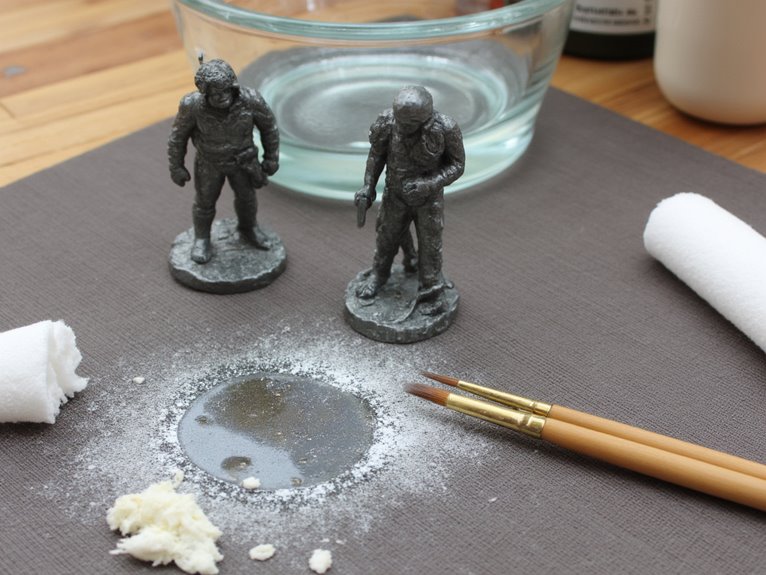

While chemical strippers handle the heavy lifting of paint breakdown, effective removal requires mastering complementary mechanical and thermal techniques that complete the stripping process.
Manual scraping with toothbrushes, pipe cleaners, and toothpicks dislodges softened paint from detailed surfaces. Files and sanding sticks remove stubborn residues where glue bonds persist.
Ultrasonic cleaners provide agitation without physical abrasion, making them ideal for delicate resin miniatures. Multiple treatment cycles improve results on heavily layered paint.
Common pitfalls include applying excessive heat that warps plastic components or using inadequate soaking duration. Well-ventilated workspaces prevent harmful fume exposure during extended stripping sessions. Nitrile gloves provide necessary protection when handling chemical stripping agentsa throughout the removal process.
Effective strategies involve controlled heat gun application at low settings and proper container selection for solvent preservation. Gel-based removers offer superior control on vertical surfaces and prevent runoff during application.
Post-soak rinsing removes residual materials, while magnification aids facilitate thorough cleaning of intricate details.
Safety Precautions and Protective Equipment
Since paint strippers contain aggressive chemicals that can cause severe burns, respiratory irritation, and eye damage, you’ll need thorough protective equipment before beginning any stripping project.
Proper glove selection requires chemical-resistant materials like butyl rubber or neoprene—latex gloves won’t protect against aggressive solvents. Safety goggles shield your eyes from splashes and airborne particles during scraping.
Essential protective measures include:
- Chemical-resistant gloves made from butyl rubber or neoprene
- Safety goggles to prevent eye contact with splashes
- Long-sleeved clothing and closed-toe shoes for skin protection
- Respirators when using solvent-based strippers indoors
Ventilation importance can’t be overstated—work outdoors whenever possible. If working indoors, open all windows and doors to create cross-ventilation.
Use fans to direct fumes away from your breathing zone. Taking breaks in fresh air helps minimize inhalation of fumes during extended use. Protect nearby surfaces with drop cloths or plastic sheeting to prevent damage from accidental drips or spills.
Factors That Affect Paint Stripping Success
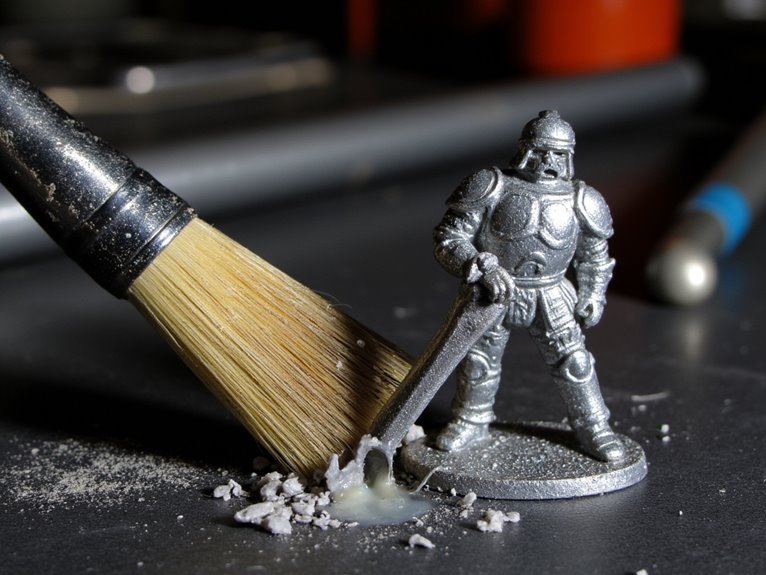

Your success in stripping paint from miniatures depends on several significant factors that you can’t ignore.
The type and age of paint you’re removing determines which stripper will work effectively—acrylic paints respond differently than enamels, while older, fully-cured coatings resist standard solvents more than fresh applications.
The miniature’s material composition and how well you’ve prepared its surface also play important roles in determining whether the paint lifts cleanly or clings stubbornly to detailed areas. Operating temperature significantly influences stripper effectiveness and can be adjusted to enhance the removal process.
Paint Type and Age
Beyond the stripper you choose and the technique you apply, the type and age of paint on your miniatures fundamentally determine stripping success.
Different paint formulations respond differently to chemical treatments, while aging affects both paint sealing and adhesion properties.
Here are four critical factors affecting paint removal:
- Paint Chemistry – Alkyd paints strip easily with alkaline solutions, while styrenated alkyds require specialized chemical formulations for effective removal.
- Age-Related Hardening – Older paints undergo increased polymerization and cross-linking, making them considerably more resistant to standard solvents and requiring aggressive treatments.
- Layer Thickness – Multiple coats create complex removal challenges, often necessitating repeated applications or mechanical assistance for complete paint elimination.
- Surface Bonding – Extended curing time strengthens paint-to-miniature adhesion, reducing stripper penetration and effectiveness markedly.
Material and Surface Preparation
Three fundamental factors beyond paint characteristics determine stripping success: the substrate material itself, its surface condition, and your preparation methods.
Metal miniatures present different adhesion challenges than resin or plastic models. Surface treatment dramatically affects paint bonding strength. Sandblasted or textured surfaces create mechanical anchoring points that increase removal difficulty by 40-60% compared to smooth finishes.
Conversion coatings on metals form porous films that allow paint penetration below the surface layer. You’ll encounter stronger bonds on surfaces with microscopic roughness or chemical etching.
Preparation involves evaluating surface texture and previous treatments. Smooth, untreated surfaces allow easier paint lifting. Carved details and textured areas require different stripping approaches.
Your material compatibility determines stripper selection—caustic solutions work well on metals but may damage certain plastics or resins.
Eco-Friendly and Biodegradable Alternatives
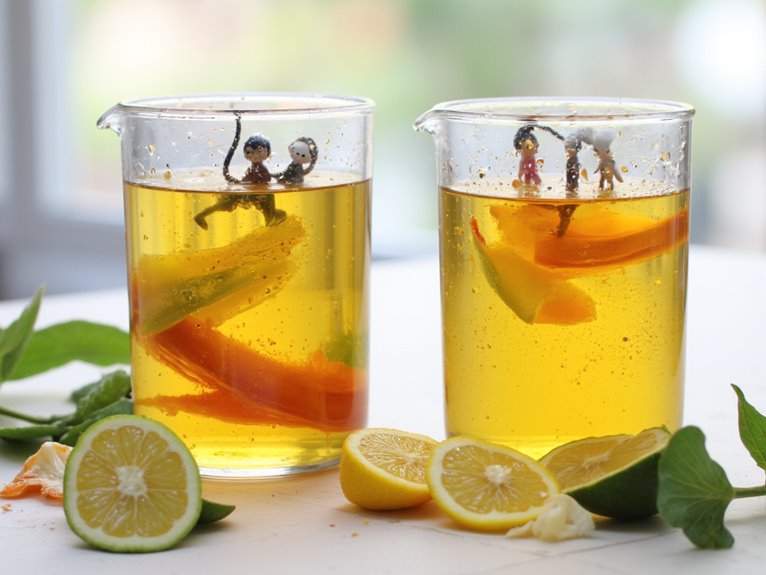

You can protect both your health and the environment by choosing eco-friendly paint stripping alternatives that perform just as effectively as traditional chemical solvents.
Biodegradable solutions like soy-based removers offer non-toxic performance, while mechanical methods such as sanding and heat guns eliminate chemical exposure entirely.
Water-based gentle techniques provide the safest approach for delicate miniatures, requiring longer working times but delivering superior safety margins for indoor use.
Biodegradable Stripping Solutions
As environmental consciousness grows within the miniature painting community, biodegradable stripping solutions have emerged as powerful alternatives to traditional chemical paint removers.
These formulations eliminate toxic compounds like methylene chloride while maintaining excellent stripping performance. You’ll find coverage rates of 175-225 square feet per gallon with fast-acting results.
Key biodegradable components include:
- Soy methyl ester – derived from soybean oil for strong degreasing power
- Benzyl alcohol – bio-based solvent without harsh fumes
- Organic acids – adipic, glutaric, and succinic acids for safe stripping
- Water-based carriers – non-flammable formulations reducing fire hazards
These solutions meet environmental regulations while providing versatile substrate compatibility.
You can apply them via brush, spray, or immersion methods depending on your project’s complexity and miniature size requirements.
Mechanical Removal Methods
Mechanical paint removal transforms the stripping process by eliminating chemical hazards while delivering precise results on miniature surfaces. You’ll find these methods release no volatile organic compounds into your workspace environment.
Mechanical Sanding offers excellent control on metals, plastics, and wood surfaces. Fine-grit sandpaper removes paint through physical abrasion without chemicals. Wet sanding minimizes airborne dust particles considerably.
Rotary tools with soft brush attachments provide precision for tight spaces on resin miniatures.
Infrared Removal heats paint layers from within, causing detachment without surface damage. This method operates 60% faster than traditional techniques while producing no hazardous fumes. You can target specific areas effectively.
Abrasive blasting uses biodegradable media like baking soda or walnut shells. These eco-friendly materials create pressurized streams that strip paint safely from composite materials.
Water-Based Gentle Techniques
Water-based paint strippers represent the safest approach for miniature paint removal while maintaining environmental responsibility.
These biodegradable solutions deliver excellent water based efficacy without damaging delicate plastic or resin surfaces. The gentle application process eliminates risks associated with caustic chemicals.
Key techniques for miniature stripping include:
- Thick Layer Coverage – Apply generous coats to guarantee complete paint penetration.
- Plastic Wrap Sealing – Cover treated miniatures to trap moisture and enhance effectiveness.
- Extended Soaking Time – Allow 2-4 hours for thorough paint dissolution.
- Soft Brush Removal – Use old toothbrushes to gently remove loosened paint layers.
Soy-based and citrus-based alternatives offer non-toxic performance comparable to harsh solvents.
These eco-friendly options protect both your health and miniature details while achieving professional results.
Tools and Materials for Optimal Results
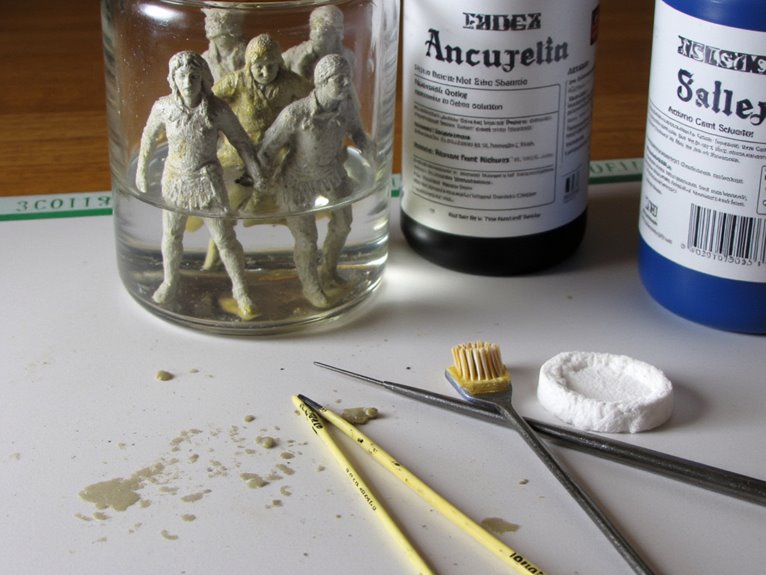
Successful miniature paint stripping depends on selecting the right combination of solvents, tools, and equipment for your specific project requirements.
Your tools selection directly impacts stripping efficiency. Plastic, copper, and stainless steel bristle brushes provide varying scrubbing intensities. Old toothbrushes excel in recessed areas where detail work matters most. Cotton buds offer precision for spot removal, while modeling knives handle stubborn paint layers.
Tool selection makes the difference between effortless paint removal and hours of frustrating scrubbing with inadequate equipment.
Material compatibility determines container choice. Glass containers resist chemical damage better than plastic alternatives, though both work effectively. You’ll need covered containers to prevent evaporation and maintain solvent strength. Multiple containers enable simultaneous processing of different materials.
Essential workspace materials include paper towels, newspaper for debris collection, and gloves for skin protection. Running water access guarantees thorough rinsing.
This all-encompassing setup maximizes stripping effectiveness while maintaining safety protocols throughout the process.
Working With Different Miniature Materials
Your miniature’s material determines which stripping methods you can safely use and how aggressive you can be during the process.
Plastic and metal models require different chemical approaches, with metal tolerating harsher solvents like acetone while plastic needs gentler treatment to prevent damage.
Resin miniatures present unique challenges that demand the most careful handling due to their brittle nature and sensitivity to strong chemicals.
Specialized formulas like AK Interactive Paint Stripper are designed to be safe for plastic, resin, and white metal surfaces while effectively removing acrylic paints and primers.
Plastic Vs Metal Models
Material composition fundamentally determines your paint stripping approach, as plastic and metal miniatures respond differently to chemical solvents and physical handling. Understanding these differences guarantees effective model preservation while maintaining proper painting techniques.
Chemical compatibility varies greatly between materials:
- Plastic models require isopropyl alcohol (99.9%) with 20-40 minute soaking times to avoid warping or melting.
- Metal miniatures tolerate stronger solvents like biostrip or brake fluid for faster paint removal.
- Acetone dissolves paint effectively on metal but turns plastic into sludge, making it unsuitable for polymer models.
- Physical handling differs as plastic needs gentle brushing while metal withstands vigorous scrubbing.
Metal models achieve near-complete paint removal with minimal staining, while plastic often retains residual discoloration that doesn’t affect detail clarity or priming adhesion.
Resin Material Considerations
While resin miniatures offer exceptional detail quality, they demand the most careful paint stripping approach of all miniature materials. Resin flexibility varies considerably between manufacturers, making chemical compatibility unpredictable. Temperature sensitivity also affects stripping success—cold conditions make resin brittle while heat can cause warping.
| Stripping Agent | Submersion Time | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| 90%+ IPA | 10-30 minutes | High for acrylics |
| Testors ELO | 15-45 minutes | Excellent, reusable |
| Mild detergent | 30+ minutes | Low for aged paint |
You’ll need 90% isopropyl alcohol for ideal results. Test inconspicuous areas first since resin formulations differ. Never use acetone or paint thinner—they’ll dissolve the material. Limit submersion to 30 minutes maximum. Use soft brushes only and rinse thoroughly afterward.
Dealing With Multiple Paint Layers and Stubborn Coatings
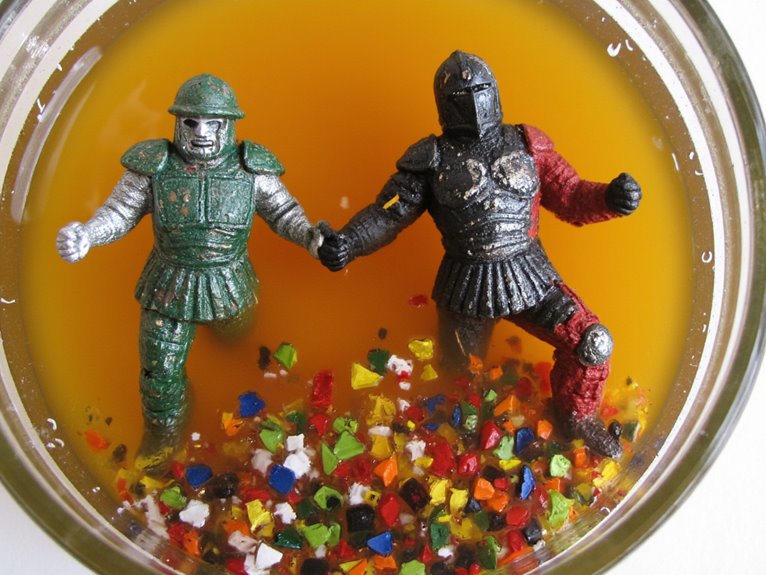

Paint accumulation presents one of the most challenging restoration scenarios you’ll encounter when stripping miniatures. Layer assessment becomes critical when determining your approach, as each coating may respond differently to removal methods.
Multiple layers create chemical barriers that prevent strippers from penetrating to deeper coatings effectively.
Thick paint buildup forms impenetrable barriers that resist chemical strippers, demanding strategic layered removal approaches for successful restoration.
Your methods comparison should evaluate these key factors:
- Chemical penetration depth – Heavy-duty strippers like Citrus Strip require thick, even application for multilayer saturation.
- Dwell time extension – Stubborn layers often need overnight treatment or repeated applications.
- Mechanical removal techniques – Brass brushes and specialized scrapers prevent surface damage during thick paint removal.
- Safety protocols – Always test older layers for lead content before beginning any stripping process.
Expect inconsistent results requiring patience and multiple treatment cycles.
Step-by-Step Stripping Process
Success in miniature stripping depends on systematic preparation and methodical execution of each phase. Begin with proper tool organization, arranging toothpicks, brushes, and Q-tips within easy reach. Select your container and guarantee adequate ventilation before handling stripping solutions.
| Phase | Duration | Key Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | 5-10 minutes | Container setup, tool organization, ventilation check |
| Soaking | 10 minutes-24 hours | Complete submersion in stripping solution |
| Scrubbing | 15-30 minutes | Mechanical removal with brushes and picks |
| Rinsing | 5-10 minutes | Clean water wash, thorough drying |
Pour your chosen stripper to completely cover miniatures. Seal the container to prevent evaporation. After soaking, observe paint bubbling before scrubbing with appropriate tools. Focus on recessed details where paint clings stubbornly. Rinse thoroughly with clean water and dry completely before inspection.
Post-Stripping Cleanup and Preparation for Repainting
Once your miniatures emerge from the stripping solution, they’ll need thorough cleaning to remove chemical residues and prepare surfaces for new paint.
Post Stripping Techniques require systematic attention to detail and surface integrity preservation.
Essential Cleanup Steps:
1. Wash thoroughly – Mix warm water with dish detergent, then scrub gently using a soft toothbrush to target crevices where residues collect.
2. Remove imperfections – Use hobby knives to scrape flash lines and apply sandpaper for smoothing, or needle files for metal miniatures.
3. Final surface preparation – Clean with isopropyl alcohol to eliminate oils and chemical residues.
Limit IPA exposure to 20-40 minutes maximum.
4. Safety protocols – Wear gloves, guarantee ventilation, and dispose of solvents properly following local hazardous waste guidelines.
For particularly stubborn residues or intricate miniatures with deep crevices, consider using an ultrasonic cleaner with gentle frequency settings to achieve thorough cleaning without damaging delicate details.
Troubleshooting Common Paint Removal Problems

Why do some miniatures emerge from stripping solutions looking worse than when they started?
Paint stripper alternatives and stripping techniques comparison reveal common failure patterns. Insufficient chemical application or inadequate dwell time causes incomplete removal. Multiple paint layers require repeated treatments. Hardened primer bonds aggressively to substrates, resisting standard strippers.
Incomplete stripping results from insufficient chemical contact time, multiple paint layers, and stubborn primer bonds that resist standard removal methods.
Metallic pigments often stain plastic surfaces permanently. Oily residues from certain chemicals necessitate thorough degreasing with soapy water. Resin miniatures suffer damage from overexposure to aggressive solvents. Always test chemicals on spare parts first.
Match your stripper to the paint type. Eco-friendly options like Simple Green work slowly but safely. Traditional solvents strip faster but pose health risks. Use stiff brushes for detailed areas. Extend soaking time for stubborn coats. Poor ventilation compounds chemical exposure dangers.
On a final note
You’ve now mastered the essential techniques for effective miniature paint stripping. Success depends on selecting the right chemical agent, following proper safety protocols, and using systematic removal methods. Remember that patience yields better results than aggressive scrubbing. Always test your chosen stripper on hidden areas first. With proper preparation, appropriate tools, and careful technique, you’ll achieve clean surfaces ready for priming and repainting every time.
